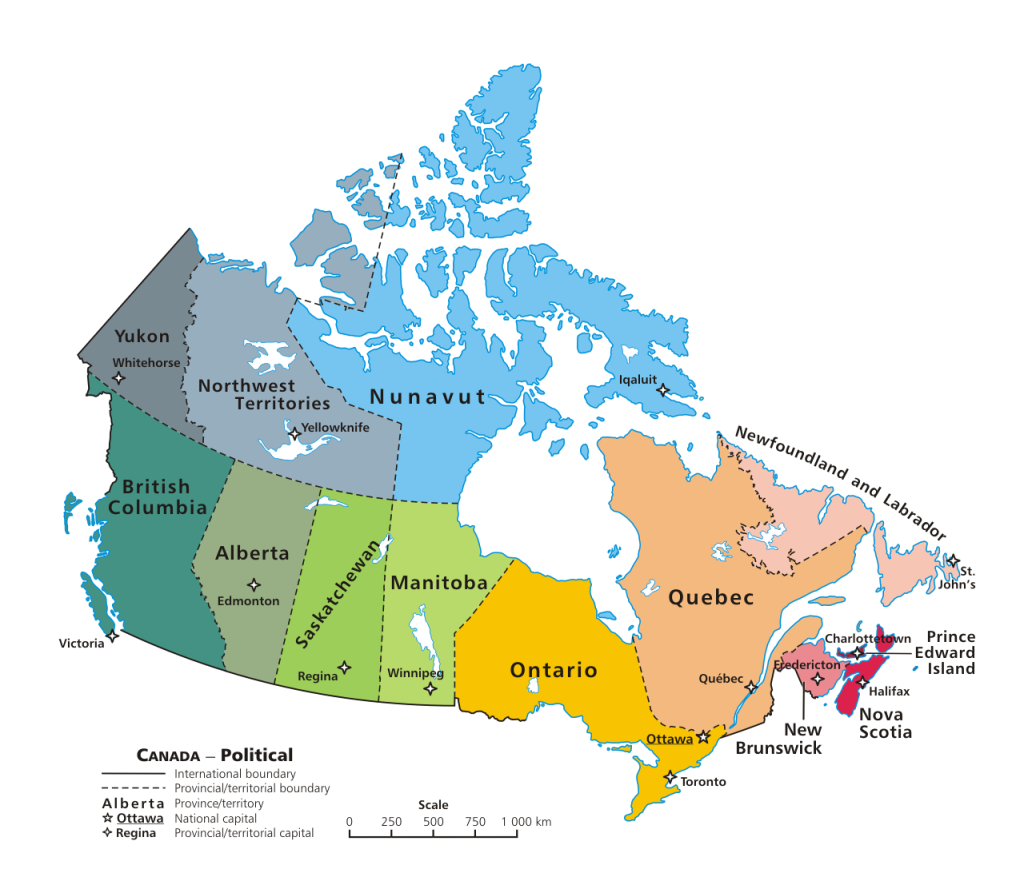
 Canada consist of 10 provinces and 3 territories. At 9.98 million square kilometers in total, Canada is the world’s second-largest country by total area, and its common border with the United States is the world’s longest land border shared by the same two countries.
Canada consist of 10 provinces and 3 territories. At 9.98 million square kilometers in total, Canada is the world’s second-largest country by total area, and its common border with the United States is the world’s longest land border shared by the same two countries.
Canada is a federal parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy, with Queen Elizabeth II as its head of state. Canada is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. The country is officially bilingual at the federal level. It is one of the world’s most ethnically diverse and multicultural nations, the product of large-scale immigration from many countries, with a population of approximately 35 million as of December 2012.
Canada is a developed country and one of the wealthiest in the world, with the eighth highest per capita income globally, and the eleventh highest ranking in the Human Development Index. It ranks among the highest in international measurements of education, government transparency, civil liberties, quality of life, and economic freedom.
Canada has a parliamentary system within the context of a constitutional monarchy, the monarchy of Canada being the foundation of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The sovereign is Queen Elizabeth II, who also serves as head of state of 15 other Commonwealth countries and each of Canada’s ten provinces. As such, the Queen’s representative, the Governor General of Canada (at present David Lloyd Johnston), carries out most of the federal royal duties in Canada.
Each of the 308 members of parliament in the House of Commons is elected by simple plurality in an electoral district or riding. General elections must be called by the governor general, either on the advice of the prime minister, within four years of the previous election, or if the government loses a confidence vote in the House. The 105 members of the Senate, whose seats are apportioned on a regional basis, serve until age 75. Five parties had representatives elected to the federal parliament in the 2011 elections: the Conservative Party of Canada (governing party), the New Democratic Party (the Official Opposition), the Liberal Party of Canada, the Bloc Québécois, and the Green Party of Canada.
Canada’s federal structure divides government responsibilities between the federal government and the ten provinces. Provincial legislatures are unicameral and operate in parliamentary fashion similar to the House of Commons. Canada’s three territories also have legislatures, but these are not sovereign and have fewer constitutional responsibilities than the provinces.
Canada’s judiciary plays an important role in interpreting laws and has the power to strike down Acts of Parliament that violate the constitution. The Supreme Court of Canada is the highest court and final arbiter and has been led since 2000 by the Chief Justice Beverley McLachlin (the first female Chief Justice). Its nine members are appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister and minister of justice. All judges at the superior and appellate levels are appointed after consultation with nongovernmental legal bodies. The federal Cabinet also appoints justices to superior courts in the provincial and territorial jurisdictions.
Common law prevails everywhere except in Quebec, where civil law predominates. Criminal law is solely a federal responsibility and is uniform throughout Canada.
Since the early 20th century, the growth of Canada’s manufacturing, mining, and service sectors has transformed the nation from a largely rural economy to an urbanized, industrial one. Like many other developed nations, the Canadian economy is dominated by the service industry, which employs about three-quarters of the country’s workforce. However, Canada is unusual among developed countries in the importance of its primary sector, in which the logging and petroleum industries are two of the most prominent components.
Canada is one of the few developed nations that are net exporters of energy. Atlantic Canada possesses vast offshore deposits of natural gas, and Alberta also hosts large oil and gas resources. The vastness of the Athabasca oil sands and other assets results in Canada having 13% of the global oil reserves, the world’s third-largest, after Venezuela and Saudi Arabia. Canada is additionally one of the world’s largest suppliers of agricultural products; the Canadian Prairies are one of the most important global producers of wheat, canola, and other grains. The Ministry of Natural Resources in Canada provides statistics regarding their major exports, zinc and uranium, and is a leading exporter of many other minerals, such as gold, nickel, aluminum, steel, iron ore, Coking Coal, and lead. Many towns in northern Canada, where agriculture is difficult, are sustainable because of nearby mines or sources of timber. Canada also has a sizable manufacturing sector centered in southern Ontario and Quebec, with automobiles and aeronautics representing particularly important industries.
The 2011 Canadian census counted a total population of 33,476,688, an increase of around 5.9 percent over the 2006 figure. By December 2012, Statistics Canada reported a population of over 35 million, signifying the fastest growth rate of any G8 nation. Between 1990 and 2008, the population increased by 5.6 million, equivalent to 20.4 percent overall growth. The main drivers of population growth are immigration and, to a lesser extent, natural growth.
About four-fifths of the population lives within 150 kilometres (93 mi) of the United States border. Approximately 80 percent of Canadians live in urban areas concentrated in the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor, the British Columbia Lower Mainland, and the Calgary–Edmonton Corridor in Alberta.
In 2006, the average age was 39.5 years; by 2011, it had risen to approximately 39.9 years. As of 2013, the average life expectancy for Canadians is 81 years.
English and French are the first languages of 59.7 and 23.2 percent of the population respectively. Approximately 98 percent of Canadians speak English or French: 57.8 percent speak English only, 22.1 percent speak French only, and 17.4 percent speak both. The English and French official-language communities, defined by the first official language spoken, constitute 73.0 and 23.6 percent of the population respectively.
Please Contact Us for more information on any of the immigration programs we offer.
